How This Website Was Built
Overview
This article explains how this website was created and full underlying logic to showcase a simplied CI/CD process.
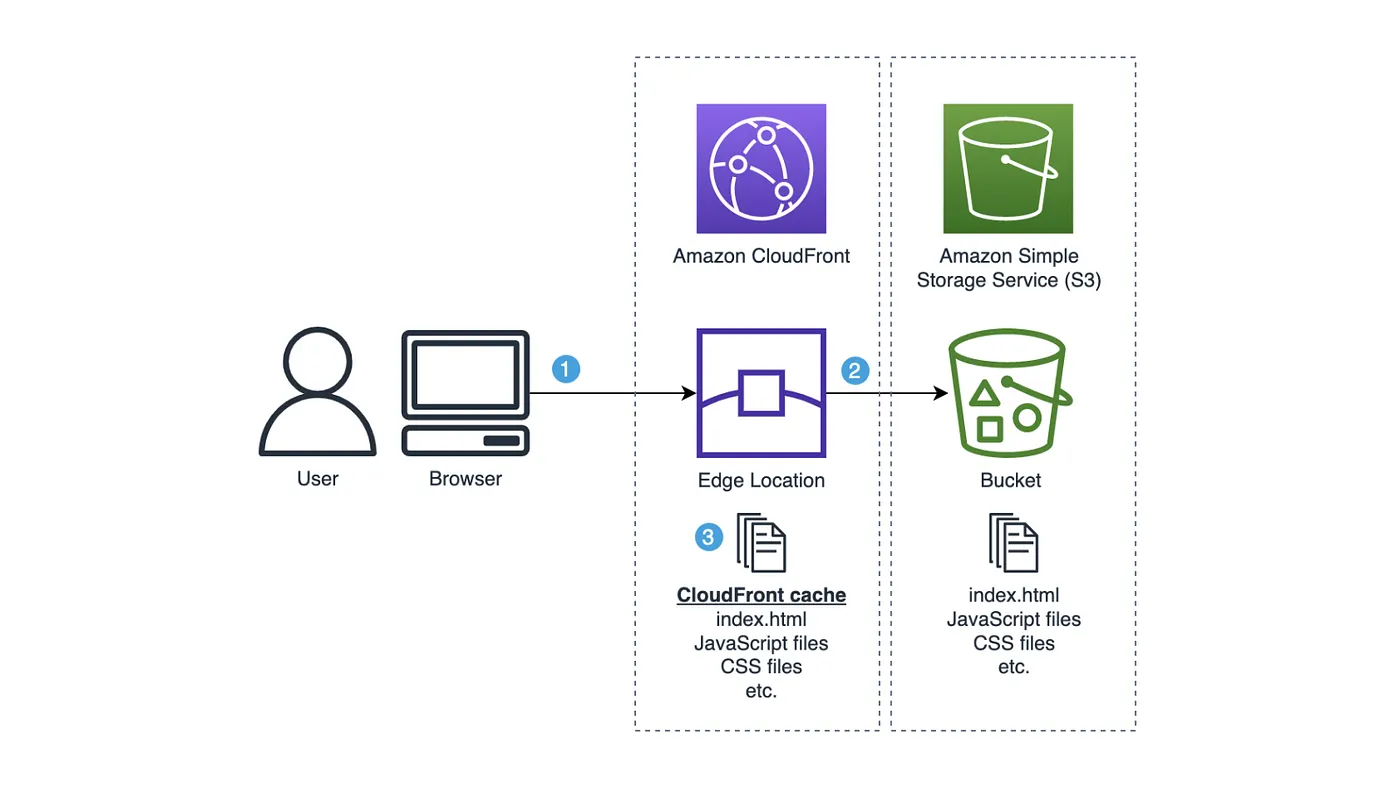
Figure 1: Infrastructure diagram
1. Use ChatGPT to generate HTML webpage
Use chatgpt to generate webpages with consistent design. Use it as a baseline template and add customized content.
2. Upload HTML file to S3
Upload generated HTML file to S3 bucket. Make it public accessible and enable static web hosting.
3. Purchase domain name
Purchase domain name (*.click is the cheapest!) in Route 53 if you don't have one already.
4. Configure AWS CloudFront
Use CloudFront to optimize performance. Add A record in Route53 and point to CloudFront.
5. Configure AWS Codepipeline
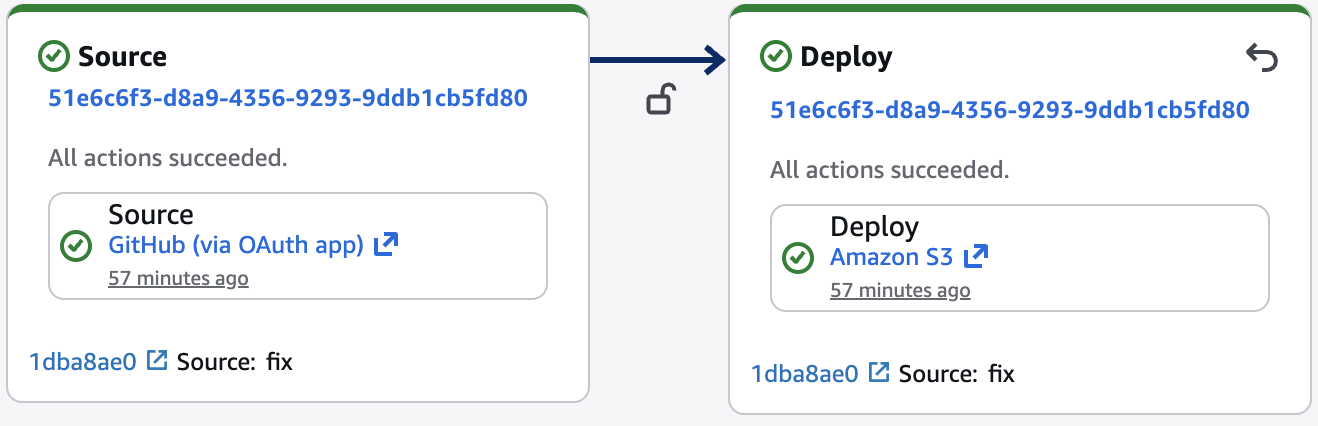 AWS Codepipeline is used to streamline any commits in Github branch, update in S3 bucket.
AWS Lambda is also used to trigger Cloudfront invalidation, whenever there is any change in S3 bucket.
After uploading new HTML or images, a CloudFront invalidation ensures visitors see the latest version.
AWS Codepipeline is used to streamline any commits in Github branch, update in S3 bucket.
AWS Lambda is also used to trigger Cloudfront invalidation, whenever there is any change in S3 bucket.
After uploading new HTML or images, a CloudFront invalidation ensures visitors see the latest version.
Lessons Learned
- Simple, semantic HTML remains the most flexible base for static content.
- CSS variables make global design changes quick and maintainable.
- CloudFront caching requires manual invalidation after updates.
- Static sites can be professional, fast, and secure — no backend required.